The global energy landscape is undergoing a monumental shift as the world moves toward a sustainable, lower-carbon future. However, this rapid expansion brings a “dual challenge”: companies must maintain reliable energy supplies using existing infrastructure while simultaneously undertaking a huge transformation toward sustainable alternatives.
Operating within the broader Oil, Gas, and Energy industry means navigating extreme market volatility, intense capital demands, and a complex ecosystem of multinational collaborations.
Read more:3 Ways to Drive Innovation in the Energy Sector
Key highlights:
- Renewable energy is a rapidly expanding sub-sector of the Oil, Gas, and Energy industry. Its focus is on generating sustainable power from natural resources, such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power.
- The growth of renewable energy is expected to surge at an unprecedented rate, doubling the oil, gas, and energy investment, due to the increased demand for a cleaner energy source to reduce half of the emission rate by 2030 and meet the net zero goal by 2050.
- Renewable energy businesses must navigate unique accounting challenges to ensure accuracy and compliance, namely: fixed asset management, power purchase agreements (PPAs), budgeting, forecasting, cash flow management, ESG compliance reporting, and more. Therefore, optimising the complex financial processes of organisations in this sector requires dedicated industry-specific solutions.
- With 30+ years implementing financial systems for energy, utilities, infrastructure, and asset-intensive businesses, TRG International positions itself as the technological solution partner for renewable energy businesses.
Renewable energy industry: Key components, challenges, and growth trends
A brief look into the Oil, Gas, and Energy industry
Renewable energy comprises all natural resources, such as sunlight, water, heat, etc., which are readily available and constantly replenished by Mother Earth. It is a sub-sector within a much bigger and more complex industry – Oil, Gas, and Energy, which is made up of several unique and defining characteristics:
- Strategic and geopolitical significance: The industry fuels national security and global economic stability, granting it considerable geopolitical leverage and influence.
- Intense capital and time commitment: It demands extraordinarily high capital investments, paired with unusually long development timelines that can span multiple decades from initial exploration to active production.
- Inherent technical complexity: Continuous innovation is necessary to manage the high level of technical complexity across all operational stages, from initial exploration through final distribution.
- Extreme market volatility: Dramatic price fluctuations are a hallmark, with global oil prices frequently capable of moving by 50% or more within short periods. [1]
- Geography-driven operations: Operations are constrained by where the natural resources exist, often mandating work in remote, challenging, and geographically diverse environments.
- Complex operating ecosystem: The sector functions through a network of collaboration between massive multinational corporations and highly specialised service companies.
- The dual challenge:The industry is simultaneously tasked with ensuring a reliable supply of energy using established infrastructure while undertaking a massive transformation toward sustainable, lower-carbon energy alternatives.
Read more:Green Cloud: Driving ESG & Sustainable Transformation
Understanding upstream, midstream, and downstream
The industry’s core value chain is traditionally segmented into three primary areas, supported by a broader ecosystem:
| Segment | Primary Focus | Key Activities | Defining Characteristics | Examples |
| Upstream | Finding and extracting oil and natural gas reserves | Geological surveys, exploratory drilling, operating production facilities | High risk, capital intensity, significant technical complexity | ConocoPhillips, BP, TotalEnergies |
| Midstream | Transporting and storing crude oil and natural gas | Operating pipelines, processing plants, storage facilities, and transport systems | Stable, fee-based business models, requiring massive infrastructure investment | Typically Pipeline/Storage Operators |
| Downstream | Refining, processing, marketing, and distributing finished products | Operating refineries, petrochemical plants, and retail networks | Characterised by thin profit margins and close end-customer relationships | Phillips 66, Valero Energy |
Getting to know the sub-sectors
Broader industry sub-verticals include:
- Integrated companies: Firms that operate across multiple or all segments of the core value chain. They benefit from diversified revenue streams and high operational flexibility. (e.g., ExxonMobil, Chevron, Shell)
- Oilfield services: Companies providing essential specialised equipment, technology, and operational support to Upstream players. Success hinges on technical innovation and service quality. (e.g., Schlumberger, Halliburton, Baker Hughes)
- Trading and distribution: Specialists focused on the buying, selling, and global movement of energy commodities. They rely on sophisticated logistics and risk management capabilities. (e.g., Vitol, Glencore)
- Energy utilities: Businesses centred on power generation, transmission, and distribution to commercial and residential customers, a segment into which traditional oil and gas firms are increasingly expanding
- Renewable energy: A rapidly expanding sub-sector concentrating on sustainable sources like wind, solar, and hydroelectric power, representing a key focus for energy transition strategies across the entire industry
Why is renewable energy on the rise?
Despite countless geopolitical unrests and a volatile economy, the market outlook for the oil, gas, and energy industry continues to look positive with increased investments. The growth of clean, renewable energy is also expected to grow at an unprecedented rate at the same time, doubling the oil, gas, and energy investment, tipping over US$2 trillion annually. [2]
The growth stems from the increased demand for a cleaner energy source to reduce half of the emission rate by 2030 and meet the net zero goal by 2050 [3]. According to the BBVA Corporate & Investment Banking [2], renewable energy will be the fastest growing sector, with an impressive surge of 25% by 2030.
Read more:Accounting & ESG: A Winning Combo
Also according to the UN [3], “Energy is at the heart of the climate challenge – and key to the solution.” Renewable energy is not just a natural power source that can be found all around us, it is also:
- More affordable, with over 90 per cent of new renewable initiatives are now cheaper than fossil fuel alternatives
- Energy efficient, especially for AI and data centres, which typically eats up the power equivalent of 100,000 homes
- Healthier as it helps address series of health issues related to climate change and air pollution
- Providing many new job opportunities as the industry needs more workers to take on new roles, for instance, in manufacturing electric vehicles or hyper-efficient appliances
- Good for the economy. In 2023 alone, clean energy sectors drove 10 per cent of GDP growth [4]
All in all, clean power is expected to surpass fossil fuel generation in the coming years. Nevertheless, renewable energy/ clean power businesses are required to make significant investments into innovation efforts to ensure their sustainability, both operationally and financially.
With hefty financing is already poured into high-priced fixed assets, heavy machinery and the likes, combined with long ROI (oil investigations can take years to yield results), unpredictable external risks, it makes efficient financial management even more crucial for this special sector.
The nuances of managing finances for renewable energy businesses
Optimising the complex financial processes of renewable energy businesses requires dedicated industry-specific solutions. When organisations maintain an efficient operation and gain full visibility into all finances, they can better allocate resources towards sustainable practices, projects, or new innovation ideas.
Read more:4 Must-haves for Oil and Gas Accounting Software
The renewable energy sector offers significant potential, but businesses must navigate unique accounting challenges to ensure accuracy and compliance, namely:
Project costs & asset management
- Multiple Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) per project make consolidation difficult
- Intercompany transactions (loans, dividends, management fees) are manually reconciled
- Asset capitalisation, depreciation, and revaluation across plants are complex
- Lack of real-time visibility into equipment performance (turbines, panels, inverters)
- Unplanned downtime leads to lost generation and revenue
- Maintenance schedules are reactive, not predictive
Revenue recognition & power purchase agreements (PPAs)
- Long-term PPAs require complex deferred revenue recognition and contract tracking
- Variations in tariffs, feed-in tariffs (FiTs), or market pricing affect revenue accuracy
- Actual vs. expected energy output not tracked accurately
- Data from SCADA or monitoring systems not integrated with finance
Budgeting & forecasting
- Budgets are static and not aligned with real-time production or energy yield
- Forecasting is often spreadsheet-based, prone to error
- Overspending during construction phase due to poor tracking of procurement, labour, and contractor costs
- Weak control over budget-to-actual variance during EPC (Engineering, Procurement, Construction)
Read more:Budgeting Challenges Facing the Oil and Gas Industry
Cash flow & treasury management
- High CAPEX and debt servicing create liquidity pressure
- Difficulty tracking loan covenants, interest, and repayments across SPVs
- Manual cash pooling and forecasting
ESG & compliance reporting
- Difficulty collecting and consolidating ESG performance metrics (carbon offset, renewable output, social impact)
- Manual data gathering across sites and systems
- Frequent audits and reporting requirements (IFRS, sustainability, energy authorities)
- Manual consolidation of data for regulatory submissions
Read more:The A to Z of Sustainability Reporting to Reach Your Green Goals
Procure-to-Pay (P2P) & expense management
- Manual procurement, invoice processing, and vendor approval cycles cause delays
- Limited visibility into supplier performance and spend categories
Moreover, renewable energy is still an emerging industry that lacks strict regulations and standardisations as well as benchmarks across different regions. On the other hand, businesses in this sector, just like any others, produce an overwhelmingly large amount of data daily. Most of them is fragmented data from financial, operational, and other systems, thus can be challenging to interpret and analyse.
A uniform method of measuring and reporting renewable energy production supports the making of more informed decisions on how to utilise these clean power sources more effectively. Fortunately, organisations can mitigate these challenges, ensure accurate and compliant financial management with robust solutions.
How TRG brings value to renewable energy organisations
TRG positions itself as the technological solution partner for renewable energy businesses that seek:
- Financial intelligence, automation, and integration
- accurate multi-entity reporting
- Project and asset cost transparency
- And seamless connectivity to operational systems
With 30+ years implementing financial systems for energy, utilities, infrastructure, and asset-intensive businesses, TRG International has successfully curated a suite of solutions to resolve your daily financial challenges head on while ensuring you stay agile and competitive.
The technology advantage
| Issues | TRG Advantage |
| Heavy architecture, rigid processes, not flexible for multi-SPV or PPA billing without major customisation | TRG solutions are modular, fast to deploy, and naturally handles SPV structures & PPA finance |
| Complex platform, long implementations, heavy dependence on consultants | TRG solutions are lightweight and can be integrated with EMS/SCADA/IoT |
| Strong in EMS/optimisation but lack financials, revenue models, carbon reporting, or PPA accounting | TRG solutions fulfil financial and reporting gaps, thus complementing EMS, not replacing it |
| Excellent IoT analytics but limited in finance, project costing, and multi-entity financial consolidation | TRG solutions provide strong global capabilities that encompass intercompany accounting, cost allocation, integrated financial consolidated, budgeting and planning, and more |
| Focused on carbon and ESG but weak in financial modelling, carbon revenue, or project P&L | TRG solutions unify financial and ESG performance metrics for better monitoring |
| No deep financials, weak procurement, cannot handle complex EPC cost structures | TRG provides solutions to help handle EPC costing, procurement automation, and WIP financial control |
The solution suite
With global solution experts based locally in Vietnam, Thailand, Cambodia, and Singapore, our solution suite comprises of solutions that work harmoniously together or individually to support your business expansion and centralised reporting architectures:
Infor SunSystems Cloud
Infor SunSystems Cloud is a powerful financial management solution. It is the core financial management solution, the backbone for all accounting activities designed to meet the complex needs of renewable energy businesses. SunSystems Cloud provides the robust framework necessary for comprehensive financial control, reporting, and analysis in a challenging and rapidly evolving industry.
Read more:How SunSystems Cloud Powers the Accounting Needs of Oil and Gas Companies
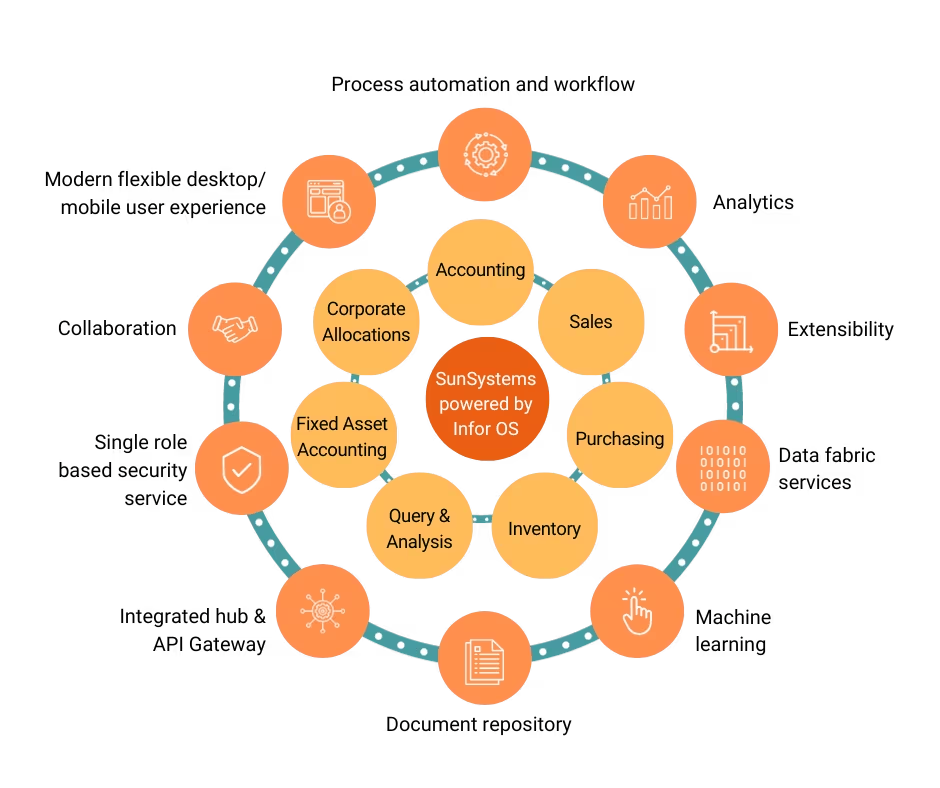
- Global capabilities: SunSystems Cloud offers multi-currency, multi-book, and multi-entity capabilities, enabling centralised financial governance while adhering to diverse local and international compliance standards (e.g., IFRS, GAAP, SOX, etc).
- Deep transactional detail: The solution is known for its highly detailed, analytical ledger architecture, allows energy companies to capture and report on financial data with granularity, linking financial transactions directly to operational data points, such as specific assets, projects, cost centres, or drilling activities.
- Agile reporting: SunSystems Cloud provides robust and dynamic reporting tools that are essential for real-time visibility into project costs, capital expenditure, joint venture accounting, and operational budgets.
- Integration and flexibility: Deployed in the cloud, it offers scalability and accessibility while ensuring seamless integration with other specialised energy-specific systems, such as asset management (EAM), forecasting, budgeting, and planning (FB&P), procurement, data management, etc.
Infor EPM
Infor EPM is a comprehensive suite of software solutions designed to help organisations plan, budget, forecast, consolidate financial data, and analyse business performance. It provides a unified platform for strategic, financial, and operational management, enabling better decision-making across the enterprise.
- Financial planning and analysis (FP&A):Infor EPM facilitates detailed budgeting, forecasting (including rolling forecasts), and multi-scenario planning. It allows renewable energy organisations to align financial plans with strategic objectives and operational realities.
- Strategy management: It supports the articulation and monitoring of strategic goals, enabling organisations to track KPIs and initiatives that drive success.
- Reporting and Analytics: Robust reporting and analytical capabilities provide users with self-service tools, dashboards, and visualisations to gain deep insights into performance, identify trends, and pinpoint areas needing attention.
For a more detailed look at Infor EPM, the “Swiss Army knife” for modern CFOs, download Infor EPM’s brochure today.
Infor OS
Infor OS stands as the core technological foundation for Infor’s industry-specific cloud solutions, driving digital transformation and enhancing business efficiency. It is a unified, intelligent platform that connects Infor and non-Infor applications, creating a seamless and integrated digital environment.
- Connectivity and integration: At its heart, Infor OS provides robust integration capabilities, eliminating data silos and creating a single source of truth for the organisation.
- User Experience (UX) and Extensibility: The platform delivers a modern, consumer-grade user experience through its central interface, which is consistent across all Infor applications. It also offers powerful tools for personalisation and extensibility, allowing users to tailor the workspace to their specific roles and for developers to build custom applications that leverage the OS foundation.
- Data management: Infor OS centralises data management, feeding information into analytics and business intelligence tools.
- Security and scalability: As a cloud-native platform, Infor OS is built on a highly secure and scalable infrastructure, ensuring business continuity, meeting stringent industry compliance requirements, and easily accommodating future growth and expansion of the organisation’s digital footprint.
Watch this on-demand webinar to learn practically all you need to know about this operating backbone.
Yooz
Yooz is a cloud-based, AI-powered procure-to-pay (P2P) automation solution that automates every step from purchase request to payment.
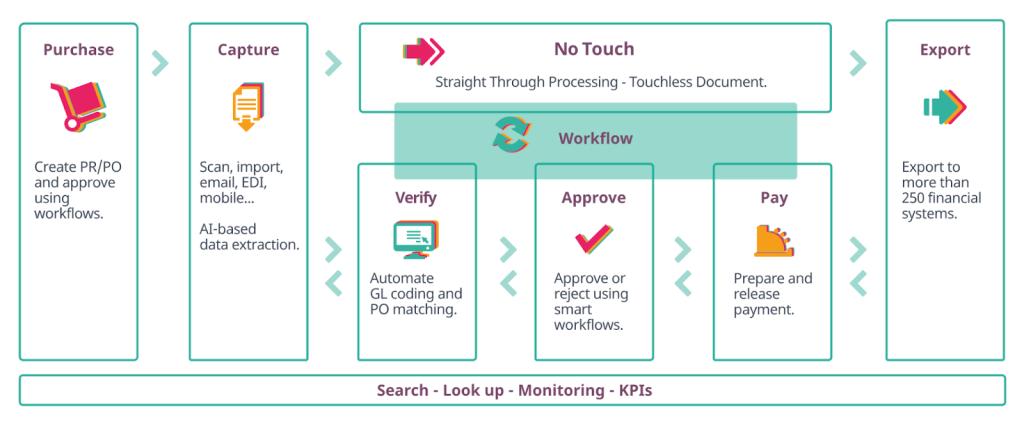
The solution eliminates common inefficiencies to ensure your production schedules are always on track.
- AP automation: AI-powered invoice, statements, expenses, etc. capturing, verification, approval, and more, ensuring the highest accuracy and eliminating manual errors
- P2P automation: Streamline your entire P2P process, from initial requisition through to final purchase orders
- Fraud prevention:Yooz’s AI-driven suite provides sophisticated tools for reducing financial frauds, including comprehensive fraud detection, payment integrity assurance, user authentication, and robust security measures
- Vendor relationship management: Strengthen vendor relationships with real-time data updates and prompt payments; simplify onboarding using a single email address
Sysynkt
Sysynkt leverages Open Banking APIs to connect seamlessly and instantly with banks, credit card companies, and other financial institutions. This allows for:
- Real-time transaction feeds directly into Sysynkt, eliminating manual downloading and uploading of bank statements
- Automated transaction matching, allocation postings, variance detection, and more
- Automated coding and auto-matching suggestion using predictive and rules-based reconciliation engine
- Streamlined and secure payments for better cash flow management and control
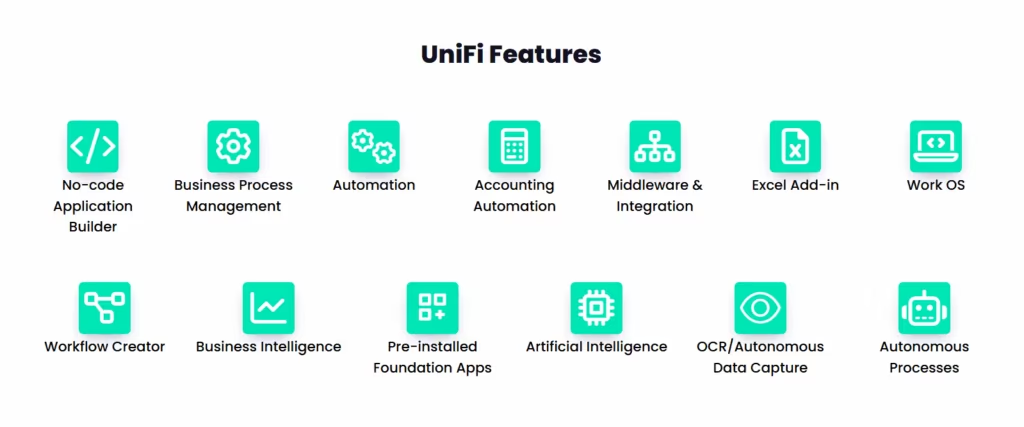
Unifi
UniFi centralises expense tracking and offers real-time visibility into spending patterns, enabling renewable energy businesses to:
- Centralise operational expense management across departments
- Simplify all travel arrangements with an integrated booking system
- Snap receipt photos and submit claims directly from mobile
- Easily consolidate multiple receipts into one single submission
- Enforce workflows to ensure policy compliance and reduce errors
The results achieved
- 2–4X faster deployments; minimal disruption to EMS/SCADA operations
- 50–80% reduction in AP processing time
- 30–40% faster month-end closing across multi-SPV portfolios
- Improved cash-flow visibility with automated PPA revenue scheduling
- Real-time EPC project cost tracking for faster identification of overruns
- 10–20% reduction in procurement leakage with automated approvals & analytics
- More accurate O&M cost allocation for solar, wind, and BESS assets
- Automated PPA billing eliminates manual errors & missed revenue
Ready for a Deeper Dive into Your Energy Needs?
We understand that navigating the complexities of the energy sector requires tailored guidance. That’s why we offer a completely personalised consultation to address your specific questions, challenges, and project goals.
Don’t wait to get the expert insights you need.SCHEDULE A QUICK, FOCUSED CALL with Kavi today!
Kavi, our lead specialist for this renewable energy vertical is ready to discuss your unique situation, explore potential solutions, and outline how our resources can be best leveraged for your success. This is your opportunity to gain clarity and define the next steps for your project.
References:
1. https://learning.sap.com/courses/introducing-the-oil-gas-energy-industry/defining-the-essentials-of-the-oil-gas-and-energy-industry
2. https://www.bbvacib.com/insights/news/energy-sector-challenges-and-opportunities-in-the-transition-to-sustainability/
3. https://www.un.org/en/climatechange/raising-ambition/renewable-energy
4. https://www.un.org/sites/un2.un.org/files/un-energy-transition-report_2025.pdf





