There is not just one type of automation, and no two automations are the same. We have all heard of the term, but that is just the typical umbrella name. Have you heard of hyper-automation? And then there is intelligent automation.
Wait, isn’t all automation… intelligent?
Read more:Transitioning to IFRS in Vietnam: Why Digitalisation is the Key to Success
Key takeaways
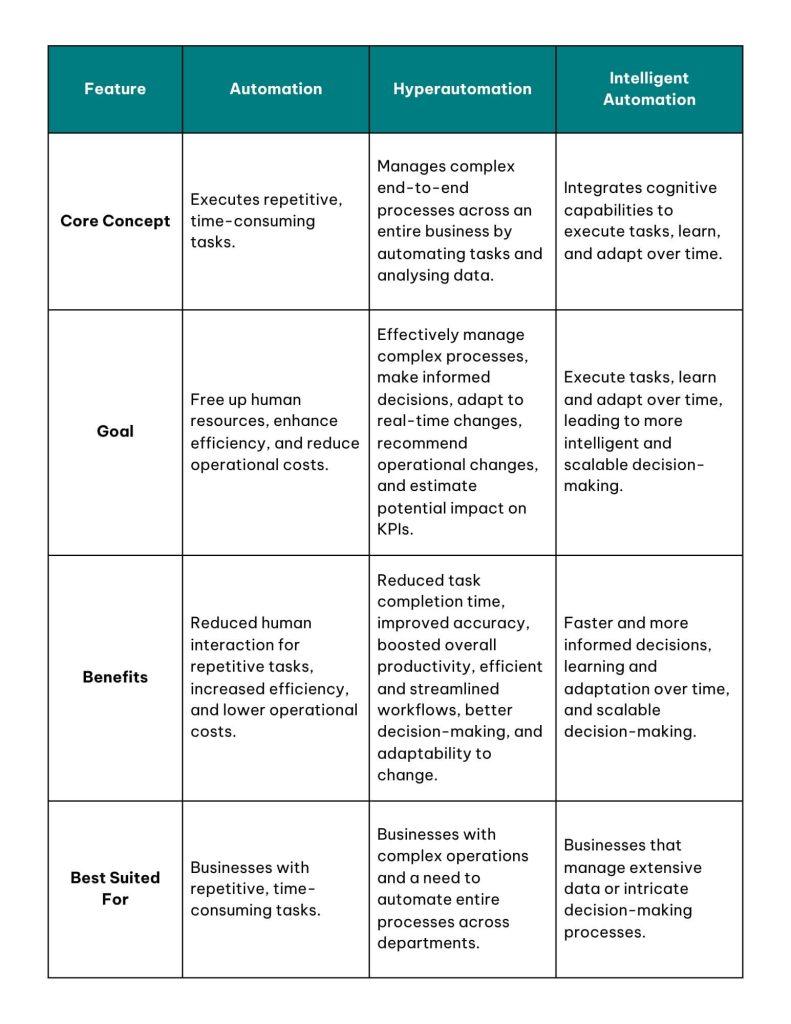
– Traditional automation focuses on executing repetitive tasks.
– Hyperautomation extends beyond single tasks to automate entire end-to-end processes.
– Intelligent automation integrates cognitive capabilities like AI, BPM, and RPA.
– The future of automation in business is presented as an opportunity for economic growth and job upskilling, with significant time savings, cost reductions, and improved productivity.
What is automation?
Automation leverages technology to execute tasks that are typically repetitive and time-consuming. The method frees up human resources to focus on more complex and strategic responsibilities, thus enhancing efficiency while allowing businesses to reduce operational expenses.
Automation use cases
Automation can be applied to various sectors, from manufacturing to customer service, financial services, and more.
Interested in learning more about automation? Check out our other articles in the series:
Tech Tidbits: What is Accounts Payable Automation?
Don’t Panic! Here’s How You Get Started with Automation
The Secret to Successful Automation? It Starts with Clean Data!
5 Reasons to Invest in Workflow Automation
What is hyperautomation?
If traditional automation is bound to a single, specific task, hyperautomation kicks things up a notch by analysing data and automating the entire process, from start to finish. Hyperautomation enables businesses to make more informed decisions and adapt to real-time changes. These systems can even recommend operational changes and provide an estimation of their potential impact on key performance indicators, such as operating costs and productivity.
This might be the first time you have heard of hyperautomation, but more than just an emerging tech, it has been identified by Gartner as one of the 10 strategic tech trends [1].
According to Gartner, “hyperautomation is rapidly shifting from an option to a condition of survival”. 85% of participants in a Gartner survey will “either increase or sustain their organisation’s hyperautomation investments over the next 12 months”, and over 56% already have four or more hyperautomation initiatives running simultaneously.
Read more:You’re Losing Money on Manual Invoice Processing! Here’s A Solution
Hyperautomation use cases
Hyperautomation is beneficial for businesses with complex operations in reducing task completion time, improving accuracy, and boosting overall productivity. It utilises advanced technologies like AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants, which leverage Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Machine Learning (ML). These components are best known for their ability to learn and adapt. Through ML algorithms and NLP, patterns, data, and preferences are continuously analysed to help improve and personalise the user experience over time.
The applications of hyperautomation can range from answering customers’ queries about product information and providing basic troubleshooting to even conducting simple banking transactions (e.g., fund transfers). Compared to traditional manual support, which is prone to longer response times and human limitations (due to fatigue, inconsistent information, or restricted availability), these AI-powered assistants can provide instant, consistent, 24/7 services.
Read more:Transforming Business Workflows at Speed: Inside Infor Velocity Suite
Beyond customer service, hyperautomation can also be used to transform financial operations, namely invoice processing, expense management, and payment reconciliation.
What is intelligent automation?
Intelligent automation (IA) is also known as cognitive automation. Yes, you are correct when guessing that the solution integrates cognitive capabilities to not only execute tasks but also to learn and adapt over time. The results are more intelligent and scalable decision-making processes throughout the business.
IA achieves this by combining 3 core cognitive technologies:
– Artificial Intelligence (AI): The most crucial component, serving as IA’s decision engine. AI analyses both structured and unstructured data to build a knowledge base and generate predictions.
– Business Process Management (BPM): BPM automates workflows to enhance the agility and consistency of business processes.
– Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA handles back-office tasks such as data extraction and form filling, perfectly complementing AI by leveraging AI insights to manage more complex tasks.
Intelligent automation use cases
Intelligent automation services are particularly beneficial for businesses that manage extensive data or intricate decision-making processes.
Let’s look at intelligent automation in finance as an example!
Finance departments are constantly facing increasing pressures to deliver more accurate and timely values. However, what the function has an abundance of are repetitive tasks like ledger journal entries, account reconciliations, etc.
Employing intelligent automation techniques can help free up finance teams from traditionally notorious time-consuming and labour-intensive tasks. For instance, financial planning processes typically involve data consolidation, budget preparation, and financial statement creation. Automation can manage these tasks, plus generate cash flow statements and highlight the right numbers on dedicated dashboards, helping executives understand liabilities and potential profitability.
Read more:TRG Partners with UniFi to Deliver Next-Gen Business Process Automation
Nevertheless, finance leaders must collaborate with the C-suite and IT teams to develop a robust automation strategy, integrating finance automation software to achieve organisational objectives. Implementing financial automation the right way is the solution to help businesses effectively manage resources and eliminate unnecessary manual work.
The tale of the 3 automation types: A brief comparison
The future of automation in business
Many resist new changes out of fear of being replaced. When Generative AI’s popularity spread like wildfire in just a matter of a couple of months last year, many office workers thought the end of their corporate lives was drawing near. However, while it is understandable that we fear the unknown, we should also look at the positive sides and significant opportunities that these new emerging technologies bring to our lives.
Did you know that about 33% of jobs available today did not exist 25 years ago? [2]
Consider the following numbers from Kissflow [3]:
– Time savings: 73% of IT leaders believe automation saves approximately 50% of their time.
– Cost reduction: 51% report that automation can reduce overall costs by 10% to 50%.
– Labour cost efficiency: 30% of business leaders attribute reduced labour costs to process automation.
– Improved talent acquisition: 61% of leaders find that process automation simplifies the selection of suitable talent.
– Economic growth: Automation can boost global GDP by 1.4% annually, leading to more relevant job creation.
– Upskilling for better jobs: 70% of professionals view automation as an opportunity to secure better, higher-paying jobs through upskilling.
These signify that automation and all the underlying tech that make it possible are not going anywhere. Moreover, they will continue to evolve at breakneck speed. As you probably see from the sections above, a common theme among the three automation types is how they strive to remove human interventions, or more specifically, the errors potentially caused by us humans, from all processes.
Read more:Don’t Panic! Here’s How You Get Started with Automation
Eliminating these manual mistakes from the equation is the key to better, faster, and certainly more accurate results for teams and the entire business.
However, what does it take to select a suitable automation solution and vendor for your business? Check out our guide below!
References:
1. https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/hyperautomation
2. https://kissflow.com/workflow/bpm/business-process-automation-statistics/
3. https://kissflow.com/workflow/bpm/business-process-automation-statistics/




